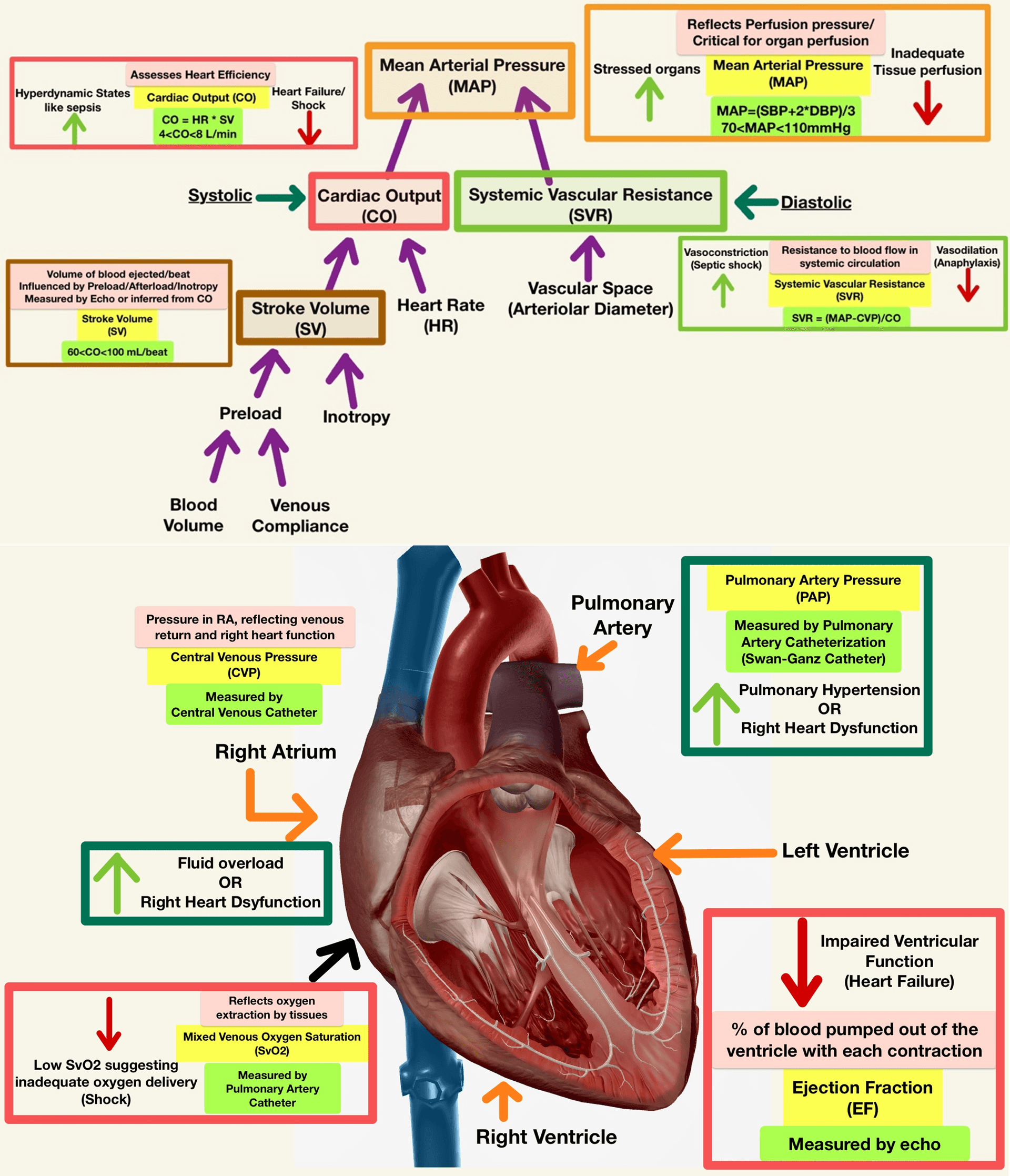
Labs
CBC Interpretation
| CBC w/o Differential | CBC w/ Differential |
|---|---|
| Routine Screening | Infection (Bacterial vs Viral) |
| Baseline evals prior to surg or meds (w/ effects on bone marrow) | Hematologic disorders |
| Basic monitoring for chronic illnesses whose WBC subtypes is not main concern | Allergic Rxns & Parasitic Infections |
| Monitoring treatment like chemo |
Quick Tips for Interpretation:
- Look at trends: Compare with previous CBCs to see if there is a stable pattern or a significant change
- Clinical correlation: Always correlate CBC findings with clinical symptoms and other diagnostic results (Labs ≠ Patient Symptoms)
- Ask about medications and recent events: Recent infections, surgeries, and medications can influence CBC results
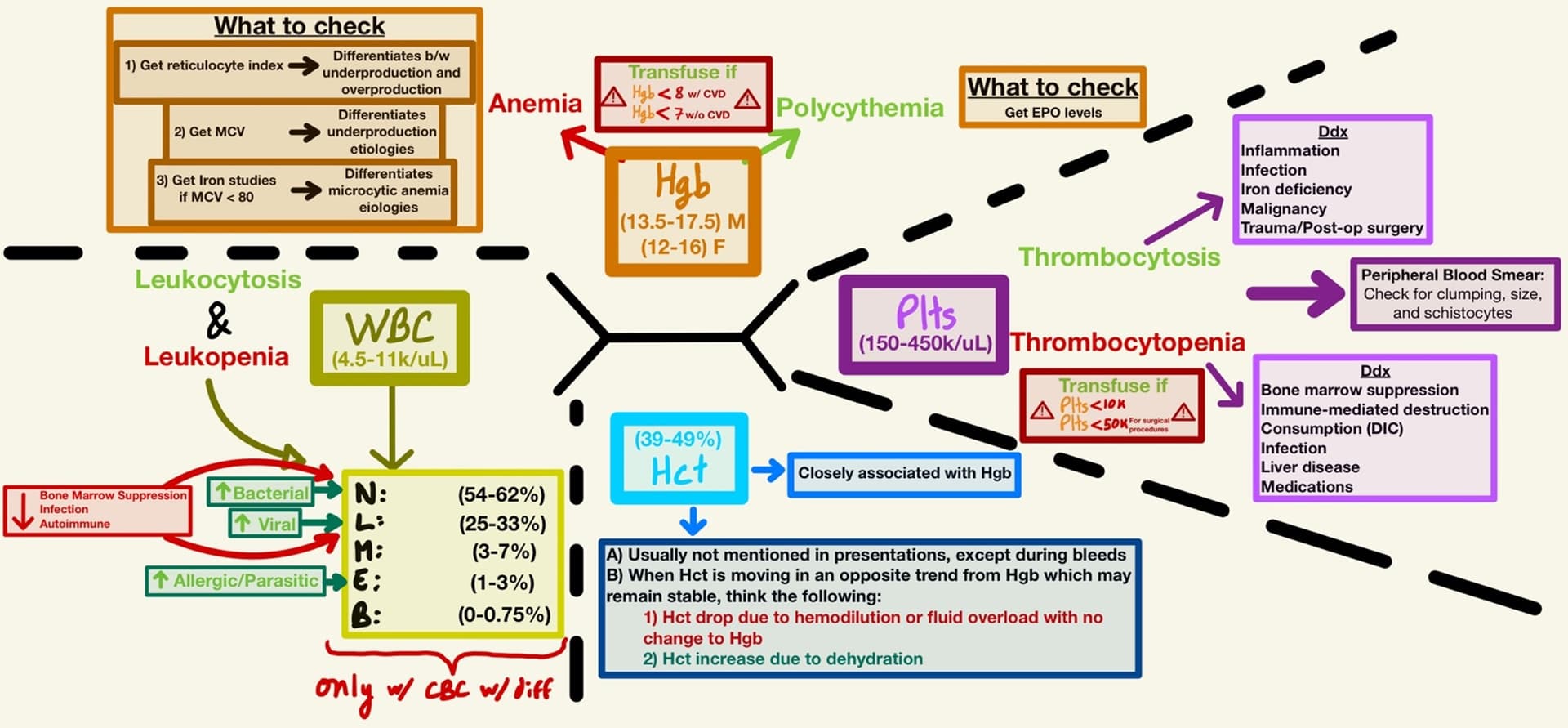
BMP vs CMP Indications
| BMP | CMP (adds LFTs) |
|---|---|
| Routine Checkups Assessing overall health status | Nutritional Status Assessment Evaluating total protein and albumin levels for malnutrition. |
| Chronic Conditions Monitoring patients with chronic conditions such as hypertension or kidney disease. | Chronic Disease Monitoring Ex: Diabetes, Liver disease, and Chronic kidney disease |
| Postoperative Monitoring Particularly in patients with known comorbidities like diabetes or chronic kidney disease, where electrolyte and renal function monitoring is crucial. | Preoperative Assessments To evaluate overall metabolic health and liver function before surgery. |
| Emergency Situations Used in emergency settings to quickly assess kidney function, electrolyte balance, and blood glucose levels. | Evaluating Systemic Illnesses To assess metabolic derangements in various illnesses. |
| Kidney Function Assessment To evaluate BUN and creatinine levels in patients with renal issues. | Liver Disease To evaluate liver function through tests like ALT, AST, ALP, and bilirubin levels. Symptoms: Jaundice, RUQ pain, hepatomegaly, or suspected liver disorders |
| Diabetes Management To monitor glucose levels in diabetic patients. | Monitoring Medication Effects Especially drugs that affect liver or kidney function. |
| Dehydration Monitoring electrolyte levels in patients with suspected dehydration. | |
| Electrolyte Imbalances Symptoms: Muscle weakness, fatigue, or arrhythmias. | |
| Acid-Base Disorders To evaluate bicarbonate levels in cases of metabolic acidosis or alkalosis. | |
| Monitoring Patients on Diuretics To check for electrolyte changes. |
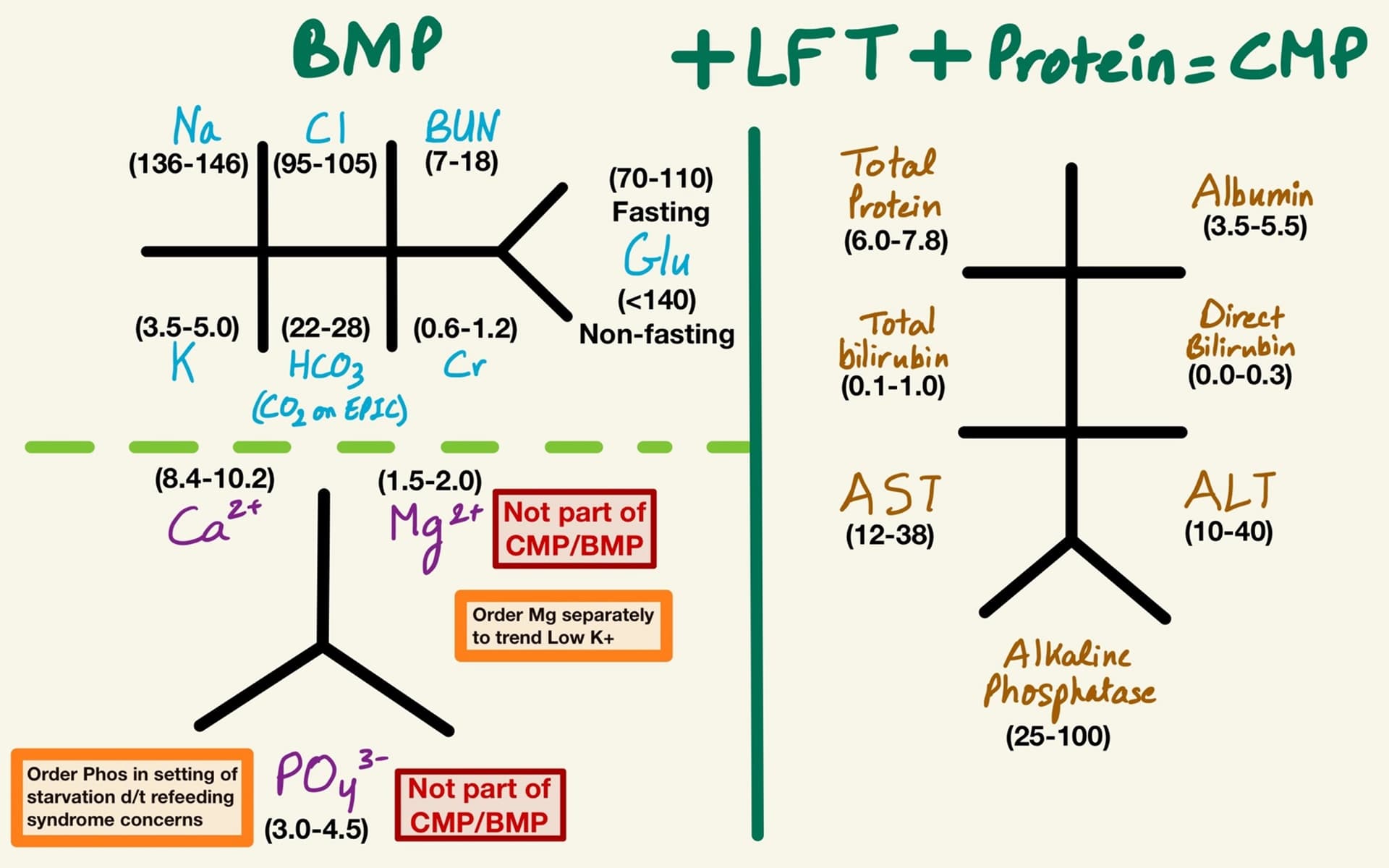
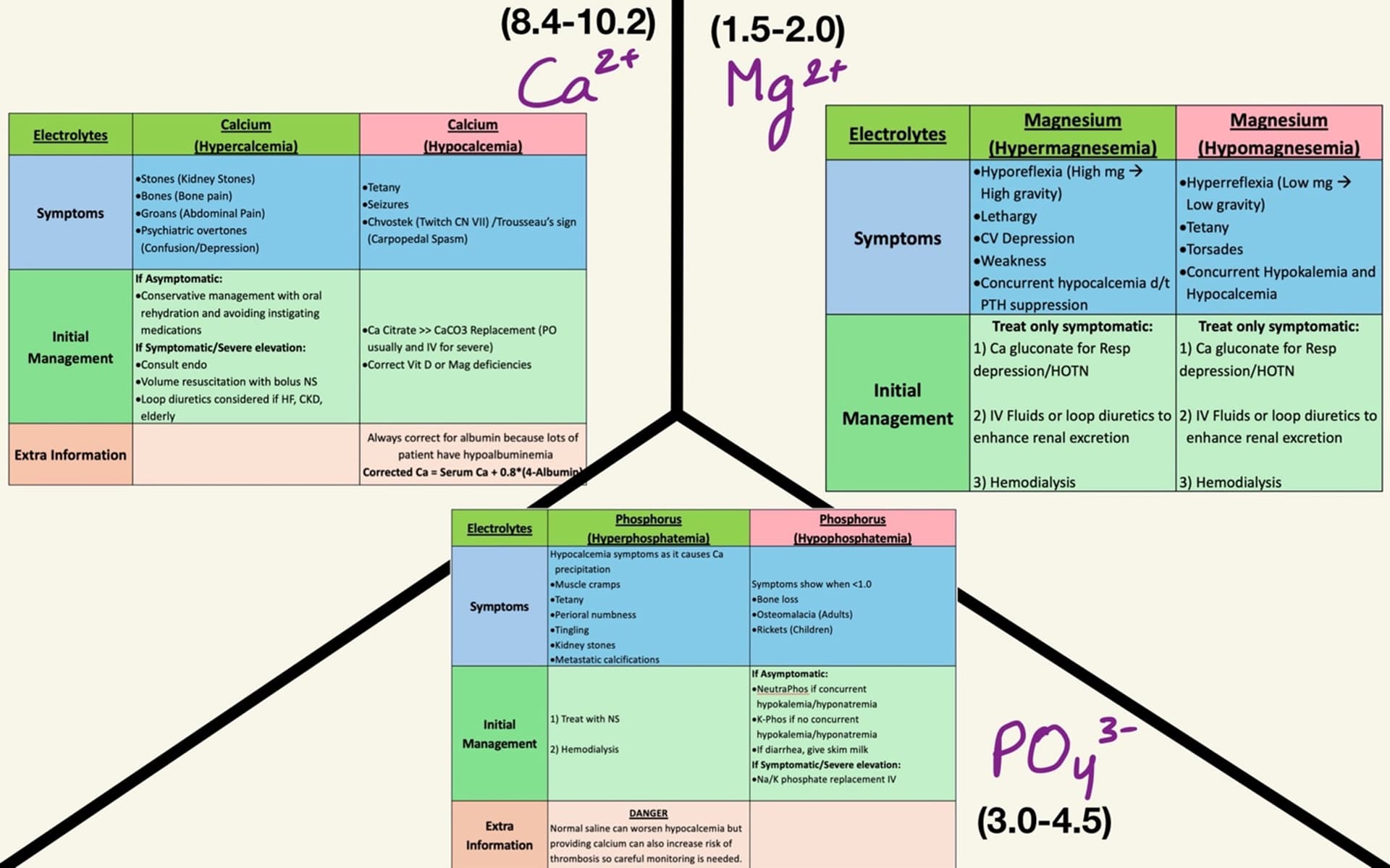
Electrolyte Basic Interpretation
Etiologies for each electrolyte deficiencies: clinicalproblemsolving.com
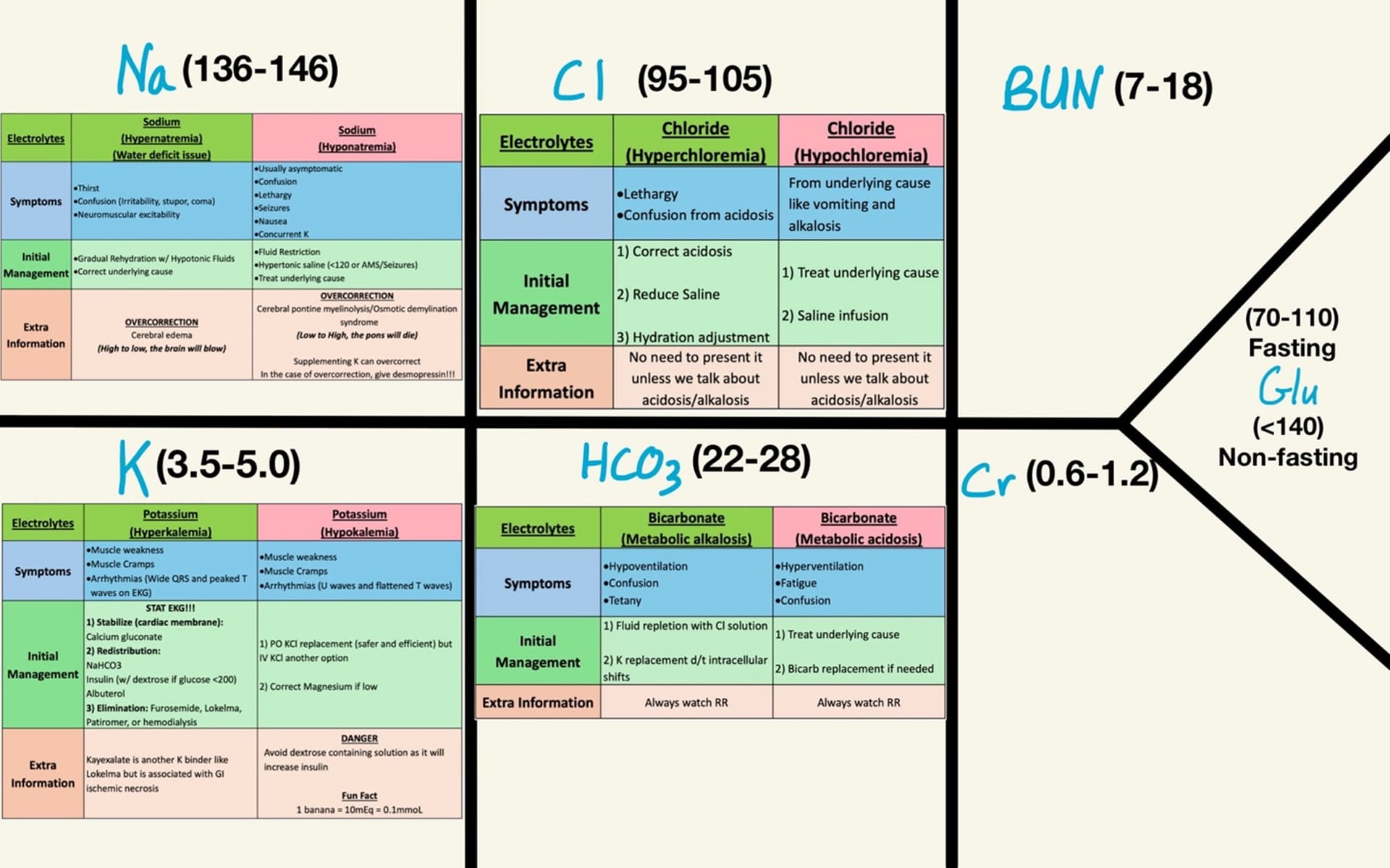
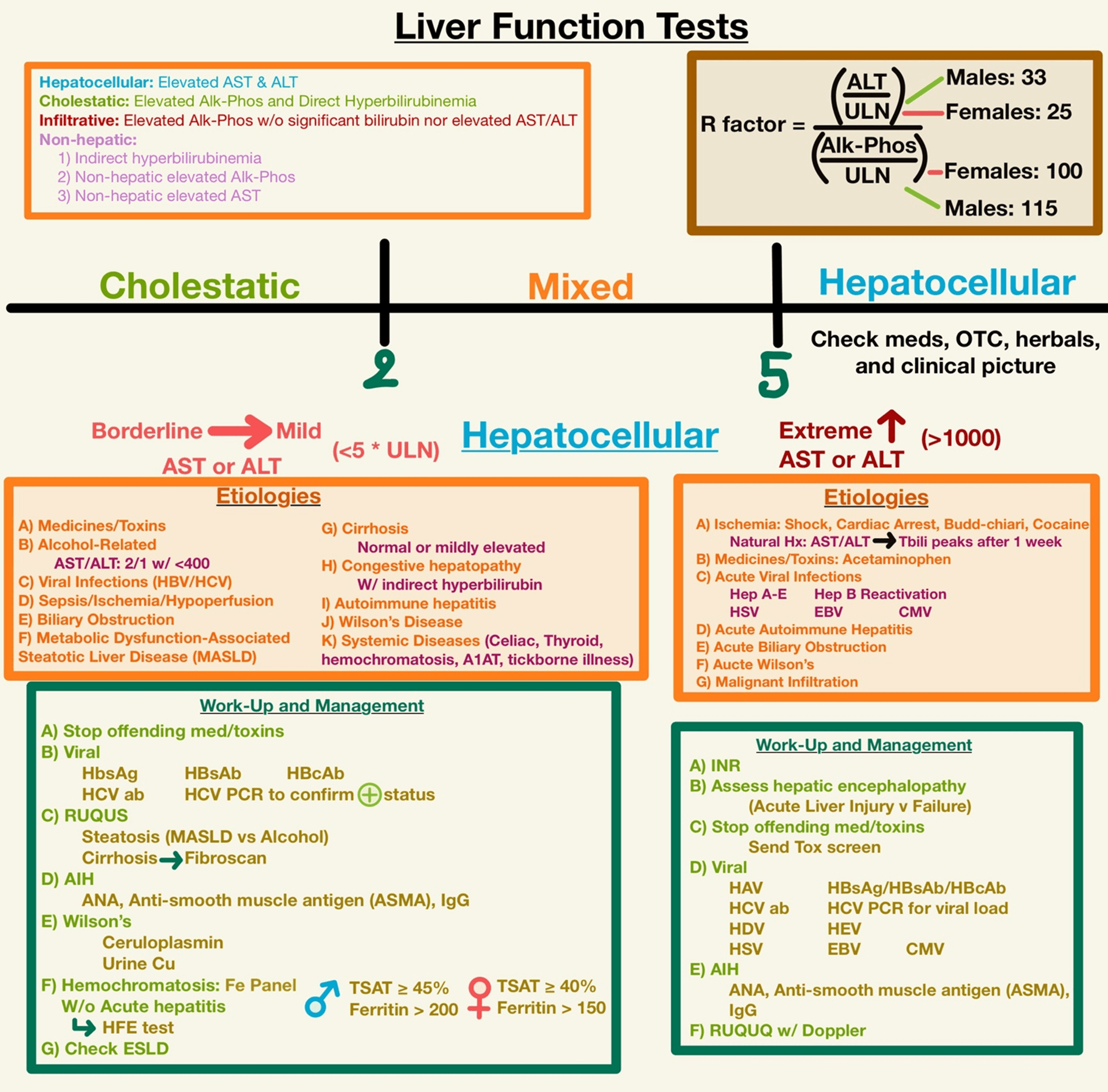
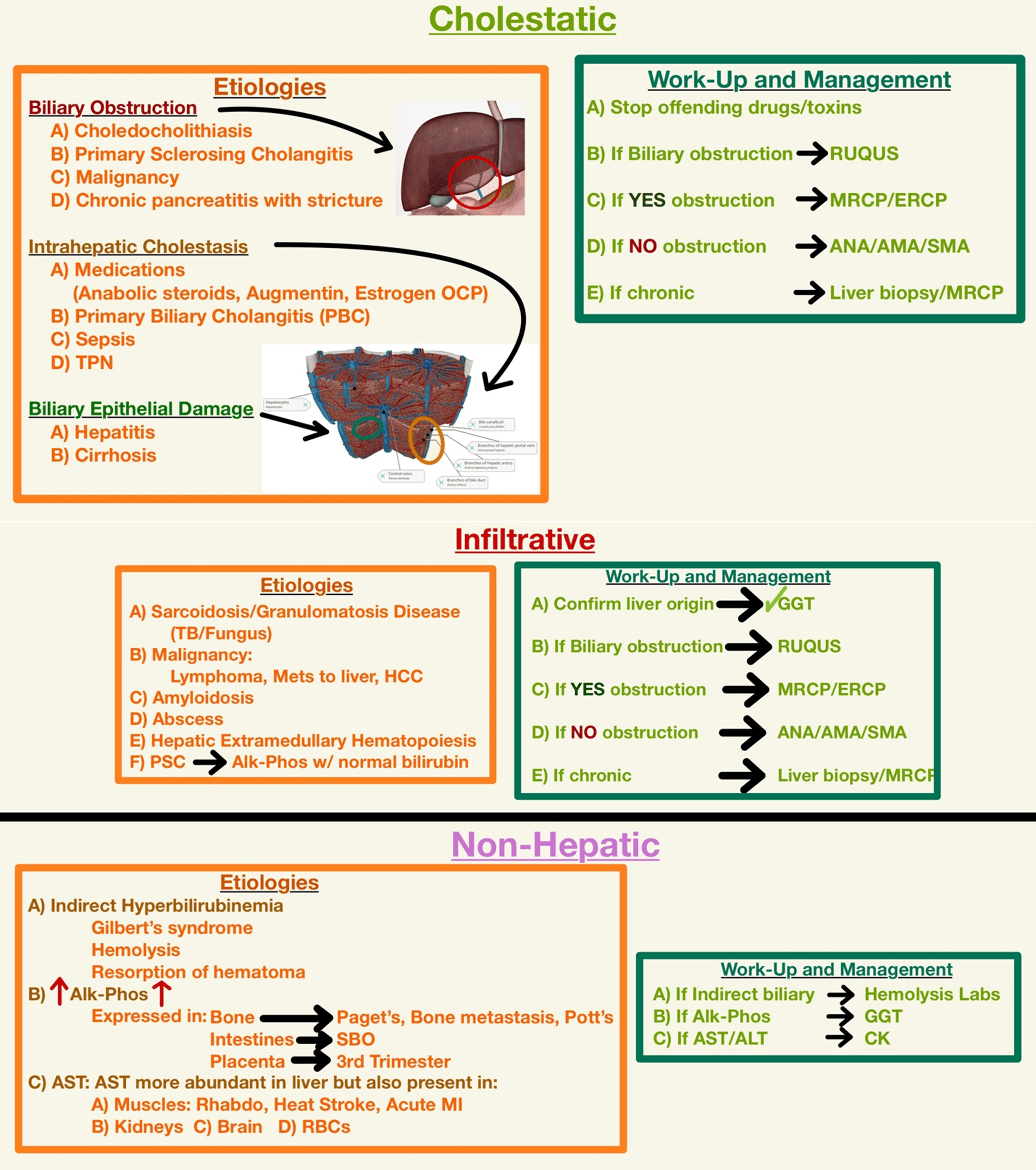
LFTs Basic Interpretation
Hemodynamic Interpretation
Clinical Integration:
- Clinical Contextual Interpretation: Consider clinical context (e.g., trauma, sepsis) when interpreting hemodynamic data
- Monitoring and Treatment: Hemodynamic monitoring guides fluid resuscitation, vasopressor use, and other interventions to optimize perfusion and cardiac function